HISTORY:
A 20 year old male with a family history of metastatic renal cell carcinoma presents with right flank pain and gross hematuria. CT workup for kidney stones reveals a renal mass measuring up to 4.9 x 3.5cm in the right lower pole concerning for malignancy. CT-guided biopsy shows clusters of spindle cells (fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells) and mature fat. Spindle cells are focally positive for smooth muscle actin, but negative for HMB-45 and MART-1. Patient undergoes right robotic assisted radical nephrectomy and regional lymph node dissection
GROSS:
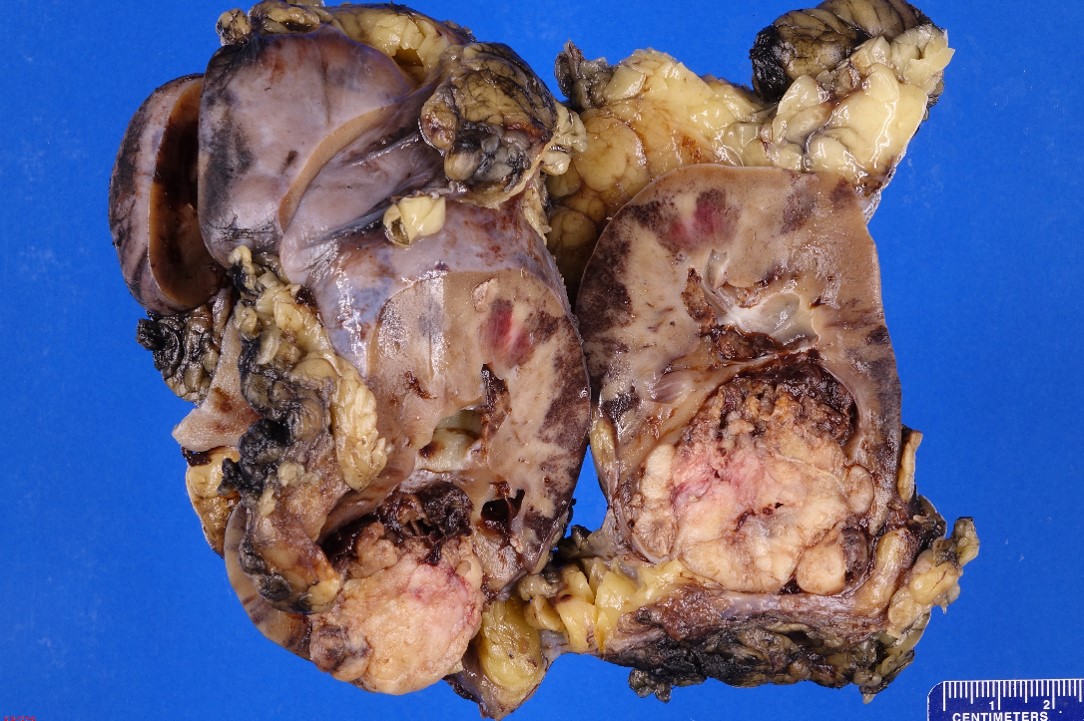
The specimen is designated “right kidney” and consist of a 13.2 x 7.8 x 6.3 cm radical nephrectomy specimen with a 2.3 cm in length and 0.4 cm in greatest diameter ureter entirely weighing 388.50 grams. There is a 0.8 cm in length and 0.3 cm in greatest diameter possible renal vein identified; it opened to reveal tan-pink, smooth vascular cut surfaces with no masses identified.
The specimen is bivalved through the hilum to reveal an 11.4 x 8.2 x 6.7 cm kidney with red-brown, unremarkable renal parenchyma with mildly dilated calyces. The corticomedullary junction is well-defined and measuring 0.6 cm and 0.7 cm respectively. Within the inferior pole, there is a 4.7 x 4.3 x 3.5 cm tan-white, firm, well-circumscribed, and partially necrotic (60%) mass that bulges into the perinephric fat but it remains confined to a possible capsule remaining 0.1 cm from the external surface. The mass bulges into the calyceal system but does not adhere to the urothelium and the scant amount of peripelvic fat is uninvolved. The mass remains appropriate greater than 3.0 cm from the ureter and hilar vasculature margins.
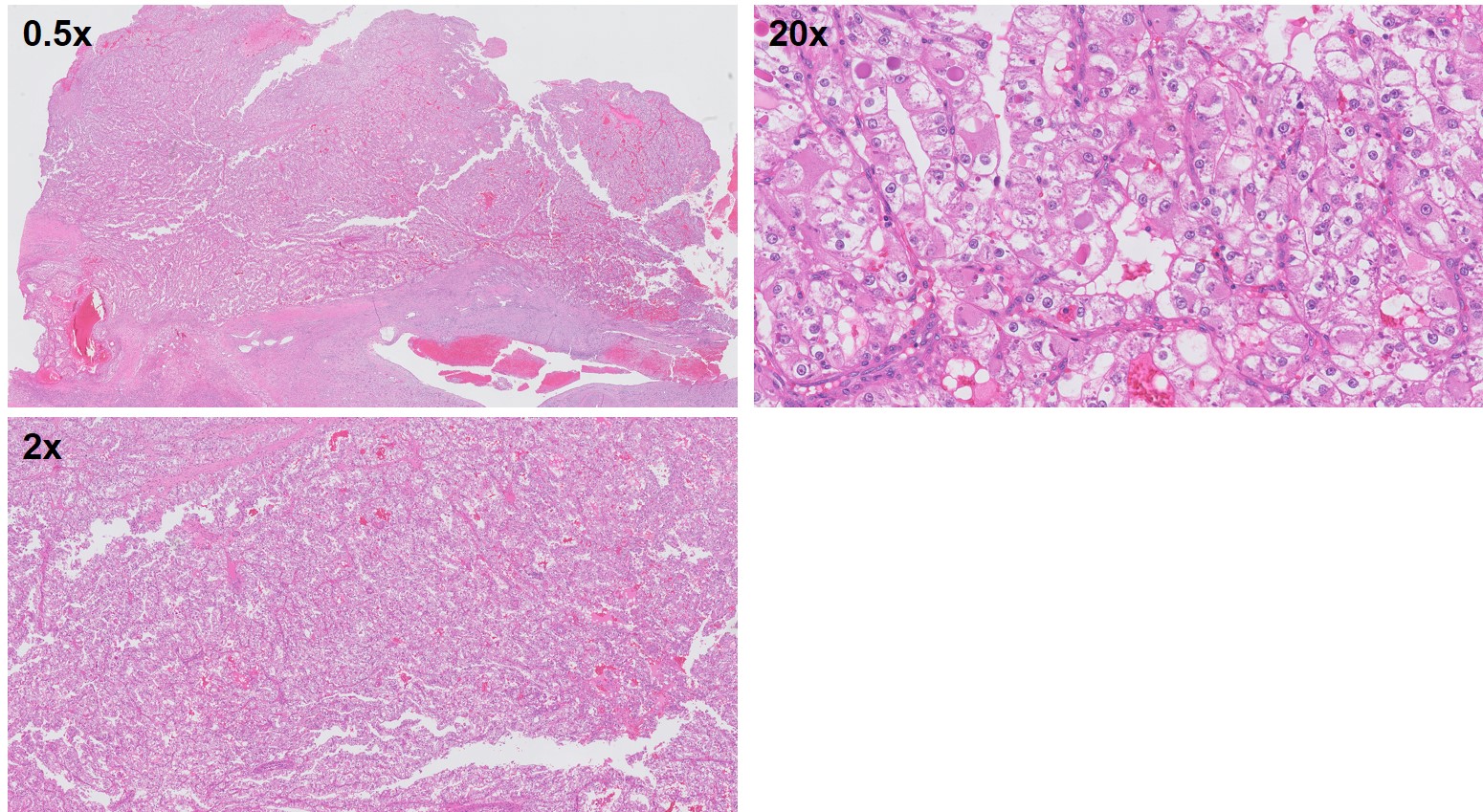
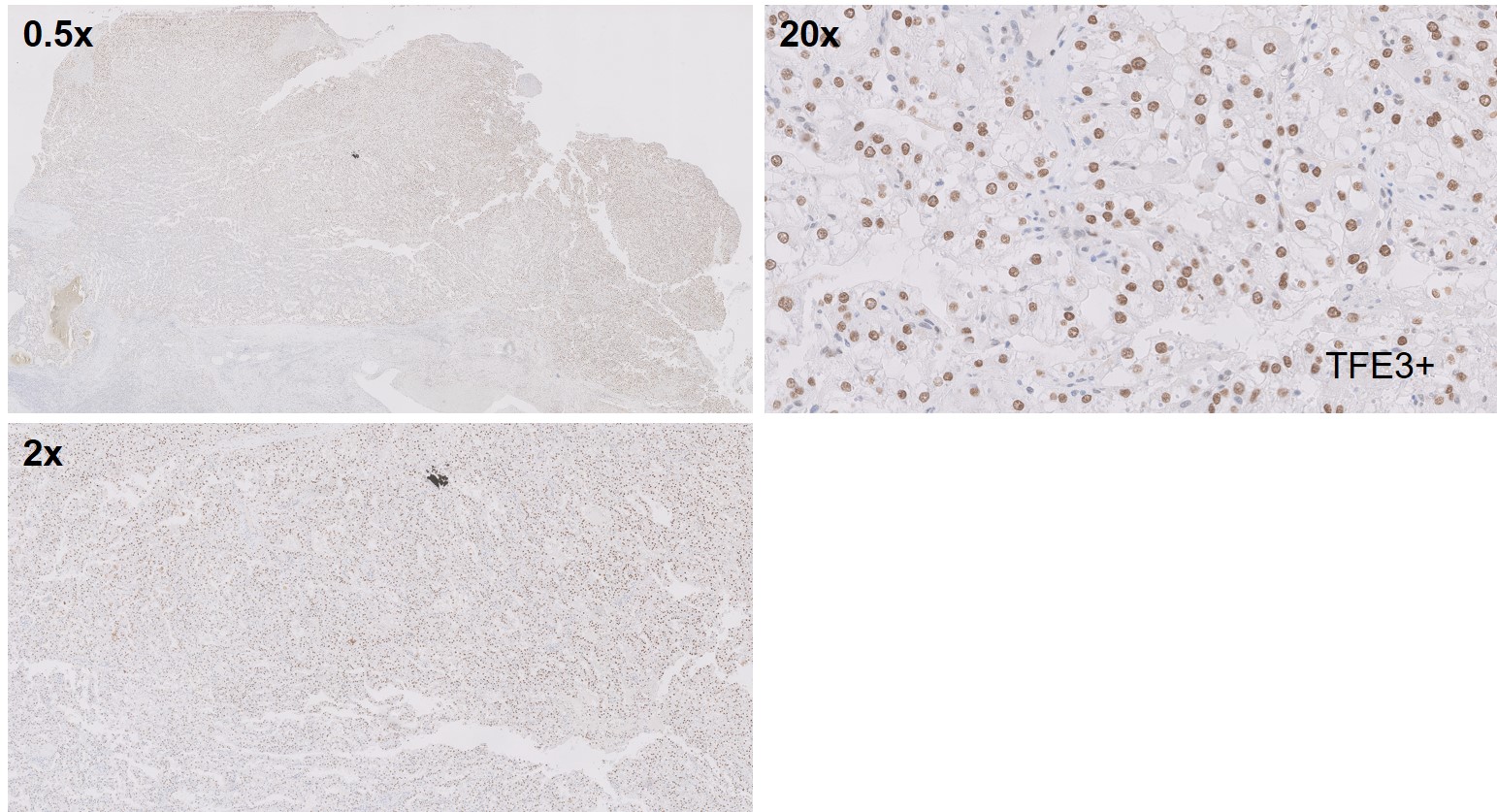
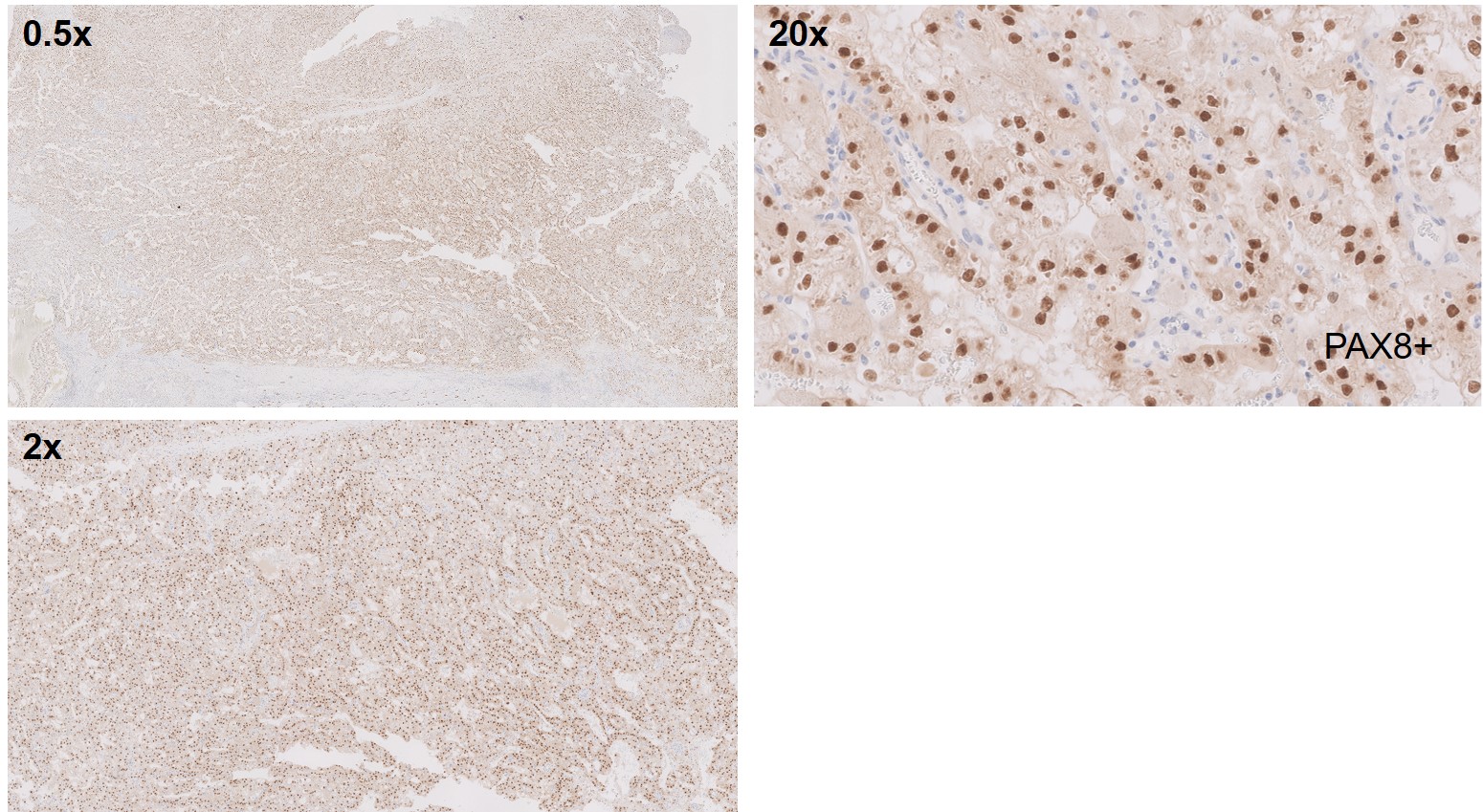
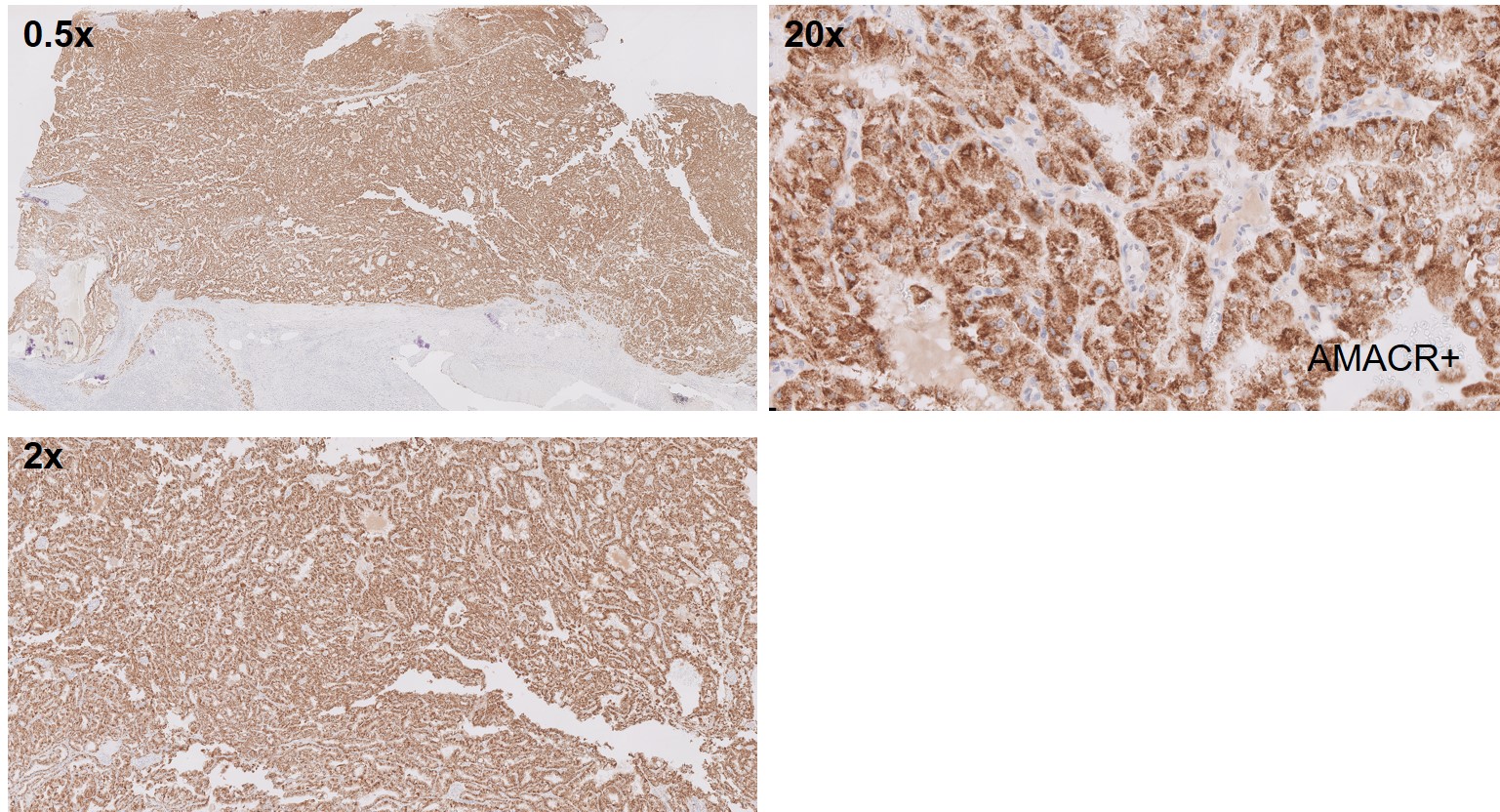
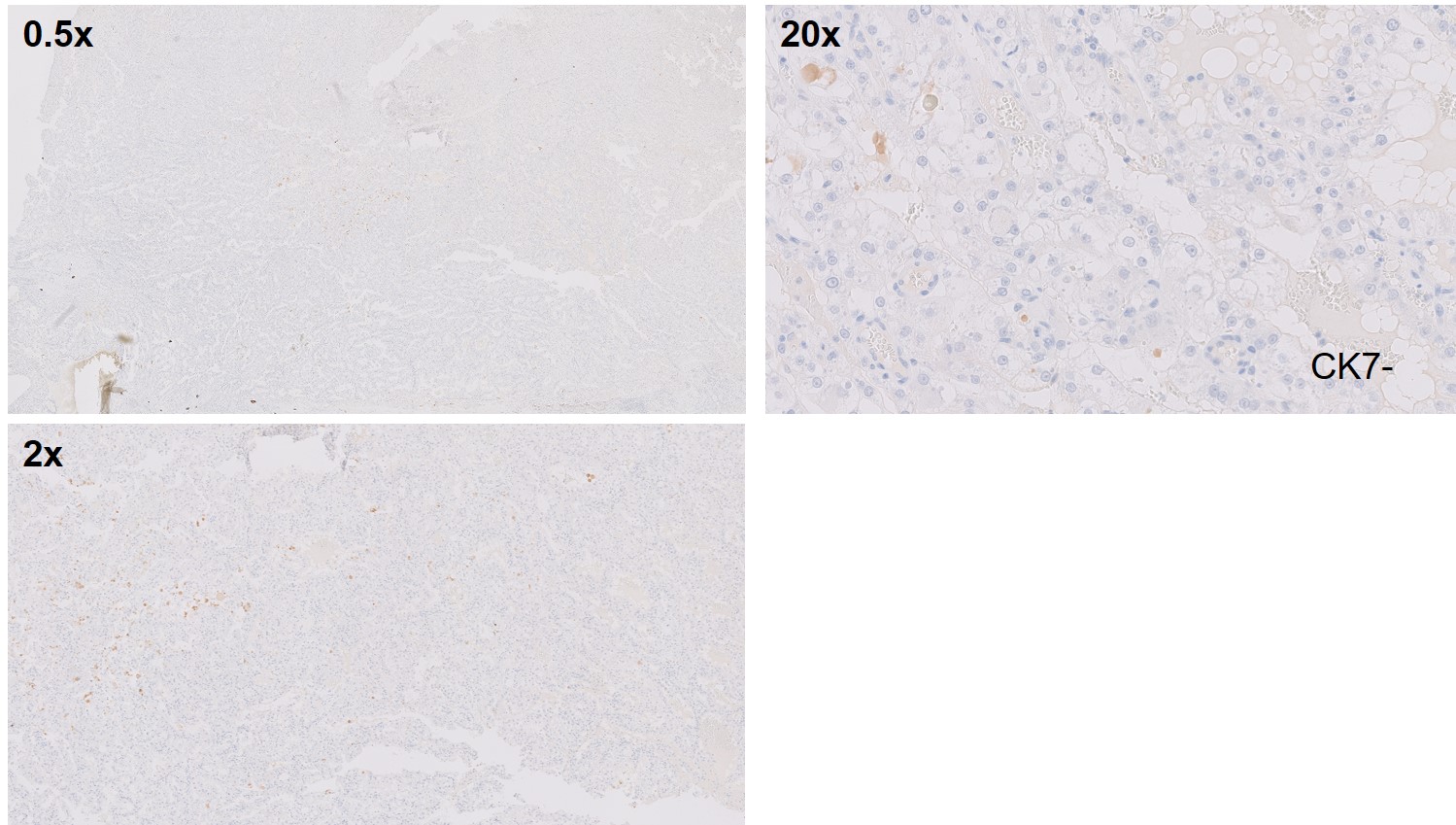
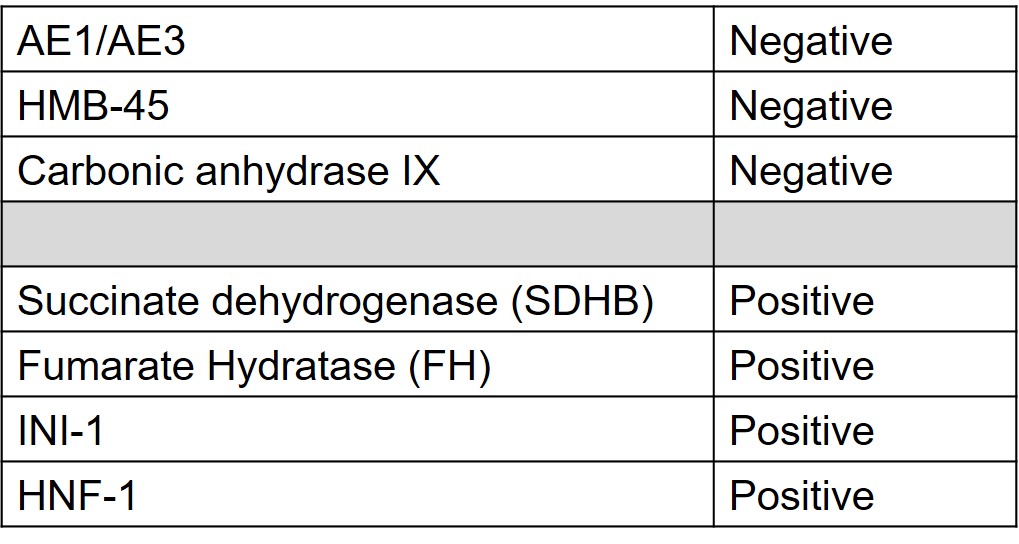
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Mucinous tubular carcinoma
- Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Translocation renal cell carcinoma
Translocation renal cell carcinomas